Earthquake-Resistant Building Design | Post-Tensioned Concrete Role
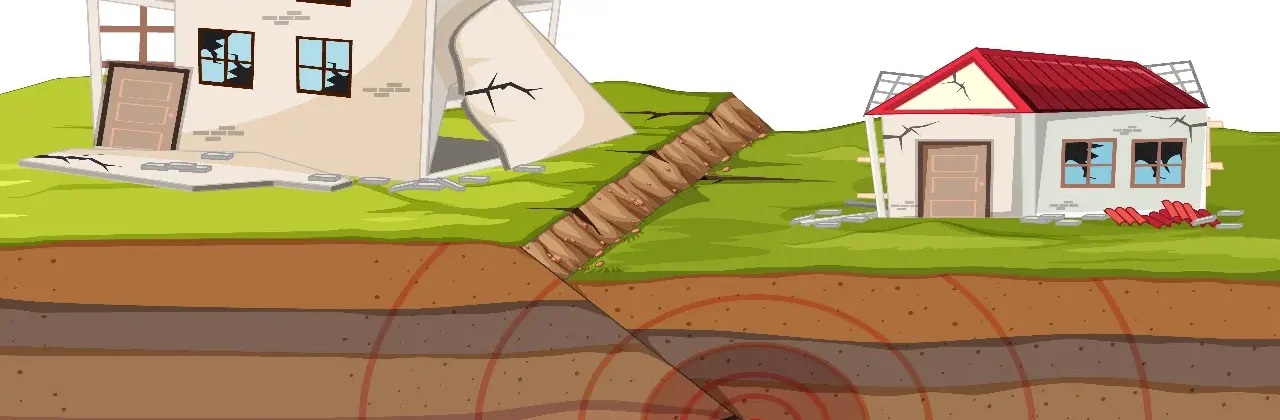
In a world of rapid geological change and an increase in the occurrence of earthquakes in multiple regions, the design of Earthquake-resistant buildings It's not just an engineering choice, it's a necessity to protect lives, property, and infrastructure. In Saudi Arabia, especially in Riyadh, which is undergoing an urbanization boom supported by Vision 2030, urban expansion requires designing buildings that combine luxury, safety, andSustainability.
Why have earthquake-resistant buildings become a necessity?
At the center of this geometric vision is the Post-tensioned concrete As a cutting-edge technology that plays a pivotal role in enhancing the durability of Earthquake-resistant buildingsenabling companies like HIMMCO to deliver innovative building solutions that meet the highest global safety standards. In this comprehensive article, we will review the design details of the Earthquake-resistant buildingsThe role of Post Tension Concrete Screwing suffixThe practical steps of implementation and the challenges facing this sector, with practical examples from HIMMCO's projects in the Kingdom.

What are earthquake-resistant buildings?
Earthquake-resistant buildings Structures that are designed according to strict engineering standards to withstand earthquake-induced ground shaking without collapsing or incurring catastrophic damage. The primary objective is to:
Protecting lives: Ensure the safety of residents and users.
Minimize physical damage: Preserve the structure of the building and its real estate value.
Continuity of functions: Enabling a building to perform its essential functions (such as hospitals or government centers) after an earthquake.
Earthquake-resistant building design principles
The design of Earthquake-resistant buildings on a range of advanced engineering principles:
Structural flexibility: Design the structure to absorb seismic energy through slight deformations without collapse.
Balanced load distribution: Ensure that lateral forces (such as earthquake forces) are evenly distributed to columns, walls, and foundations.
Use of high-performance materials: like Post Tension Concrete that combines the strength of concrete with the flexibility of steel.
Engineering code compliance: Adhere to local (e.g. Saudi Building Code SBC 301) and international (e.g. ASCE 7 or Eurocode 8) standards.
Designing strong foundations: Strengthening foundations to withstand vertical and lateral forces resulting from earthquakes.

Applied example: In a luxury residential project in Saudi ArabiaHemamco", the building was designed using moment-resistant frames supported by Post Tension Concretewhich allowed the impact of virtual vibrations to be reduced by 30% compared to conventional designs.
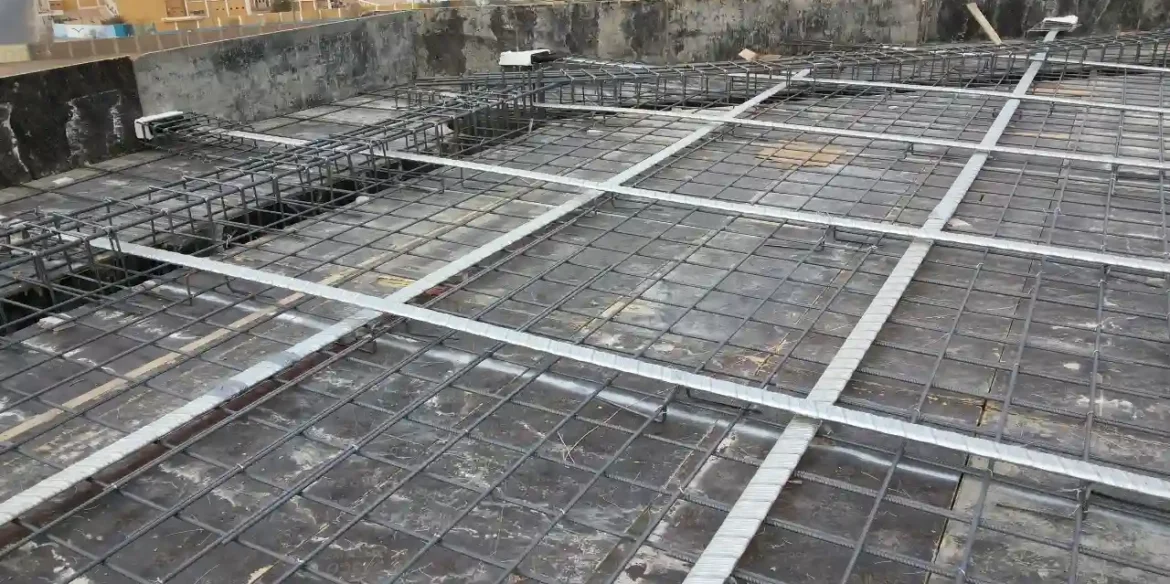
Post-tensioned concrete: A revolutionary technology for earthquake-resistant buildings
is a Post Tension Concrete (Post-Tensioned Concrete is one of the most advanced technologies in modern construction, especially in the design of Earthquake-resistant buildings. This technique involves inserting high-strength steel cables into channels in the concrete, and then tightening them using hydraulic devices after the concrete has hardened to the required strength (usually 28 days).
How does post-tensioned concrete work?
Creating internal tension: Cable tension generates a pre-compressive force in concrete, enhancing its ability to withstand the tensile forces generated by earthquakes.
Distribution of stresses: Ensures an even distribution of internal forces, minimizing the concentration of stresses in the weak points of the structure.
Strengthening flexibility: Allows the building to move slightly during an earthquake without catastrophic cracking.
The benefits of post-tensioned concrete in earthquake-resistant buildings
Reducing cracks: Reduces the appearance of cracks in tiles, walls, and columns under vibration.
Increased durability: Enhances a building's ability to absorb seismic energy without collapse.
Providing materials: Enables the design of thinner slabs and walls, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Improving structural performance: Lateral loads are better distributed, enhancing the stability of the building.
Sustainability: Minimizing material consumption contributes to reducing the project's carbon footprint.

Practical example: In a multi-story shopping center implemented by HIMMCO in Jeddah, I used Post Tension Concrete To design floor slabs with open spaces without center columns, increasing the flexibility of the interior design and enhancing the building's seismic resistance.
Comparison of conventional and post-tensioned concrete
Feature | Conventional concrete | Post-tensioned concrete |
|---|---|---|
Tensile strength | Limited, depends on weaponization | High thanks to taut cables |
Slab fish | is larger, increasing the cost | less, saving material |
Load distribution | Less efficient | More efficient and balanced |
Earthquake resistance | Good with extra armament | Excellent thanks to flexibility |
Earthquake-resistant building design steps
Design Earthquake-resistant buildings It requires a rigorous methodology that includes planning, analyzing, and implementation phases. Here are the detailed steps:
Geologic Site Analysis
Studying the soil to determine its properties (such as hardness and bearing capacity).
Seismic risk assessment based on maps of the Kingdom's seismic zones.
Determine the expected earthquake force (Peak Ground Acceleration) to design the structure accordingly.
Choosing a construction system
Tires that are resistant to torque: Provides high flexibility and is suitable for high-rise buildings.
Shear walls: Used in mid-rise buildings to distribute lateral loads.
Mixed system: Combines tires and walls to strike a balance between flexibility and rigidity.
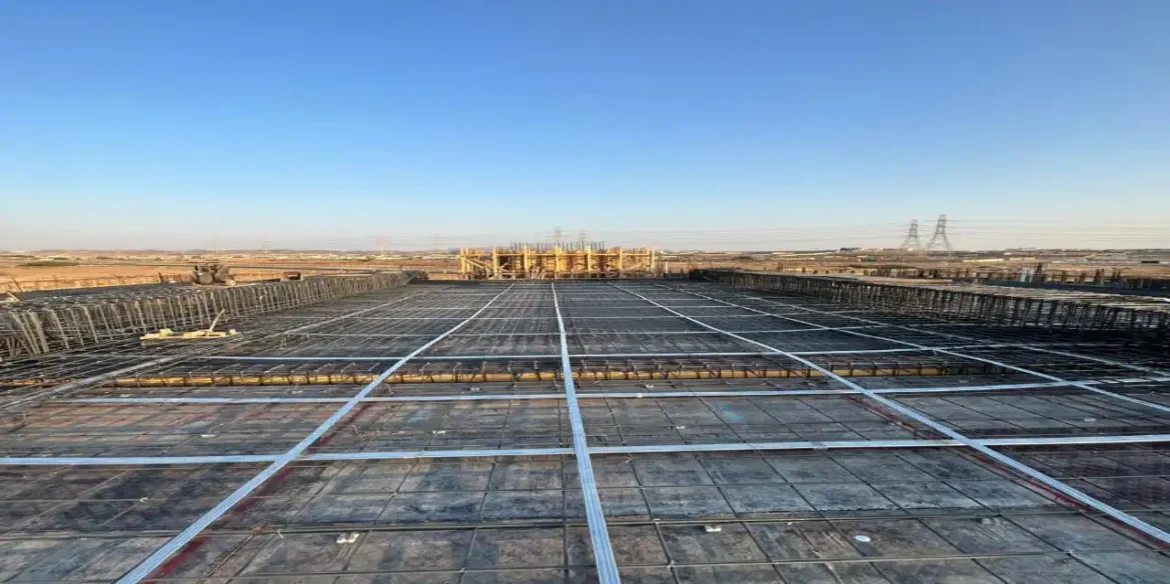
Post-tensioned concrete consolidation
Designing slabs and columns using Post-tensioned concrete To enhance flexibility.
Locating and tensioning cables based on engineering calculations.
Using advanced design programs such as ETABS or SAP2000 to simulate seismic performance.
Design by code
Adhere to the Saudi Building Code (SBC 301), which specifies seismic design requirements.
Refer to international codes such as ASCE 7 or Eurocode 8 to ensure compliance with global standards.
Supervision and implementation
Collaborate with specialized contractors in Riyadh or elsewhere in the Kingdom to execute the design accurately.
Conduct field inspections of the quality of concrete and cables before and after pouring.
Ensure timely cable tensioning using precision hydraulic equipment.
Applied example: In an office tower project in the center of Makkah, HIMMCO utilized a hybrid structural system supported by Post Tensionallowing the design of floor slabs with open spaces and high earthquake resistance, while reducing costs by 15% compared to traditional concrete.
The role of the professional contractor in the implementation of earthquake-resistant buildings
Even with a perfect engineering design, the quality of execution is the deciding factor in the success of Earthquake-resistant buildings. A professional contractor in Riyadh must have:
Post Tensioning Concrete Expertise: Ability to accurately execute tensioning stages according to engineering drawings.
Advanced equipment: Use hydraulic cable tensioners and concrete quality checkers.
Specialized engineering team: It includes civil engineers and technicians trained to deal with modern technologies.
Compliance with standards: Adherence to local and international engineering codes.
Post-Construction Services: Provide regular maintenance to check cables and anchor points.
Practical example: In a multi-unit residential project executed by HAMMCO, the company collaborated with a specialized contractor to Post-tensioned concreteDaily checks were made on the quality of the concrete and cable tension, ensuring the building's earthquake resistance to international standards.
Modern technologies: Integrating artificial intelligence into earthquake-resistant buildings
witnessed Earthquake-resistant buildings has evolved thanks to the incorporation of modern technologies such as Artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies include:
Smart sensors: Fits inside the Post-tensioned concrete To monitor tension, stretching, and deformations in real time.
Data analysis: Use artificial intelligence to analyze sensor data and predict potential structural weaknesses.
Predictive maintenance: Early detection of the need to re-tension cables or repair cracks.
Applied example: In a government project in Saudi Arabia, HEMMCO utilized smart sensors embedded in Concrete Post Tension to monitor the building's performance, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing risk by 20%.
Challenges in the design and implementation of earthquake-resistant buildings
Despite advances in construction techniques, the Earthquake-resistant buildings Multiple challenges:
High upfront costs: use Concrete Post Tension Advanced technologies may increase the initial cost, but it saves in the long run.
Lack of local expertise: The need for continuous training for engineers and technicians to deal with modern technologies.
Availability of materials: The need to import high-quality steel cables in some cases, which may delay the project.
Compliance with codes: Implementation errors resulting from not adhering to standards can lead to poor performance.
Community outreach: Lack of awareness by some developers of the importance of investing in Earthquake-resistant buildings.
Suggested solutions:
Provide government incentives to encourage the use of technologies such as Post Tension.
Establishing specialized training centers throughout the Kingdom to qualify engineering cadres.
Launching awareness campaigns to educate the community on the importance of construction safety.
Awareness and training: Building a safe future
To ensure the spread of Earthquake-resistant buildings In Saudi Arabia, the focus should be on awareness and training:
Developing academic curricula: Include design concepts Earthquake-resistant buildings in schools of civil and architectural engineering.
Hands-on workshops: Organize training courses for engineers using seismic simulation software such as Shake Table.
Community Awareness Campaigns: Launching media campaigns explaining the benefits of Screwing suffix and the importance of structural safety.
Collaboration with the private sector: Representing HMEMCO to organize educational events about new technologies.
Applied example: HAMMCO launched a workshop in Riyadh in collaboration with King Saud University, which focused on training young engineers to design Earthquake-resistant buildings Using Post Tension Concrete Screwing suffixcontributing to the qualification of 50 engineers by 2024.
Inspiring young engineers
For budding engineers and architects, the design of Earthquake-resistant buildings A challenge and an opportunity to leave a positive mark on society. Here are some tips:
Merging Art and Science: Design buildings that combine architectural beauty with engineering durability.
Continuous learning: Follow the latest developments in technologies such as Post-tensioned concrete through global courses.
Passion for innovation: Every earthquake-resistant design is an innovation that contributes to the protection of society.
Community responsibility: Remember that your work can save lives at critical moments.
In conclusion: HAMMCO builds a secure future
Design Earthquake-resistant buildings Not just a response to geological challenges, but an investment in the future of society. By relying on cutting-edge technologies such as Post-tensioned concreteHAMMCO is setting new standards for construction in the Kingdom, in line with Saudi Vision 2030.
Whether you're an investor, real estate developer, or homeowner, choosing a trusted partner like HIMMCO ensures the highest levels of security and quality. Get in touch with the HIMMCO team today for a design consultation Earthquake-resistant buildings Meet your needs and exceed your expectations!