The role of post-tensioned concrete in Saudi Arabia's 2030 megaprojects
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is witnessing a qualitative transformation in the construction and engineering sector, driven by an ambitious vision to diversify the national economy and achieve sustainable development. At the center of this transformation is post-tensioned concrete, one of the most prominent modern technologies that contributes to the implementation of large-scale and architecturally complex projects without compromising on quality and efficiency.
In recent years, it has become necessary to adopt structural solutions that meet the requirements of Saudi Arabia's mega-projects, which are not limited to infrastructure, but include towers, smart cities, bridges, and vital facilities that require high structural performance with design flexibility and economy. As the Kingdom applies strict standards within the Saudi Building Code system, the need for technologies such as Post-tensioned concrete It's more urgent than ever.
⸻
What is post-tensioned concrete and why is it revolutionizing construction?
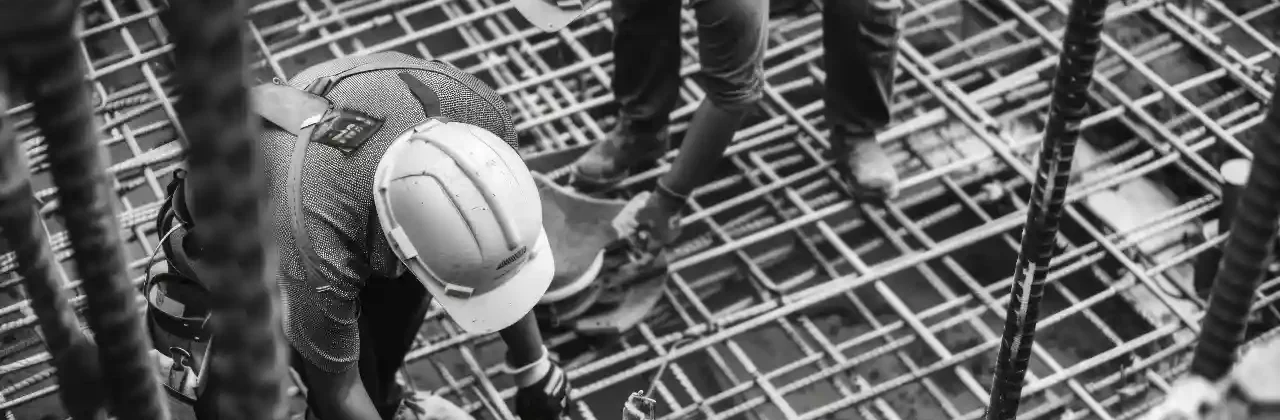
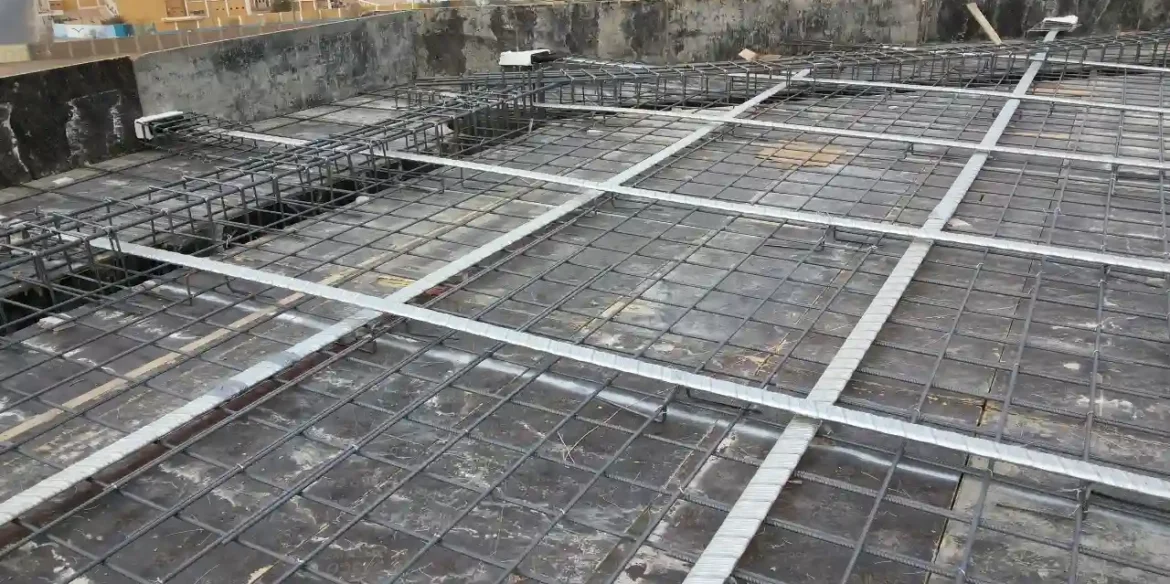
Post-Tensioned Concrete is an advanced technology used to strengthen structural elements after concrete has been poured and hardened. This is done by laying steel cables inside specialized ducts within the slabs or piles, and later tightening these cables using hydraulic devices. This process creates a counter-pressure on the concrete, enhancing its ability to withstand loads without cracks or dents.

This system differs from pre-tensioned concrete in terms of the timing of tension, but offers greater design advantages, allowing for wider opening lengths and fewer columns and partitions. Post-tensioned concrete is an ideal choice for buildings that require open interior spaces, such as malls, airports and hospitals.
Today, concrete is widely used in Saudi Arabia, not only in commercial projects, but in most components of Saudi mega-projects that require high precision in execution and adaptability to complex operational and environmental conditions.
Advantages the foundation of post-tensioned concrete technology:
- Tensioned steel cables are used inside the concrete to increase its durability.
- They allow for large openings and minimize columns.
- Reduces cracks and increases the lifespan of the facility.
- Provides better design flexibility than prestressed concrete.
⸻
Post-tensioned concrete used in Saudi mega-projects
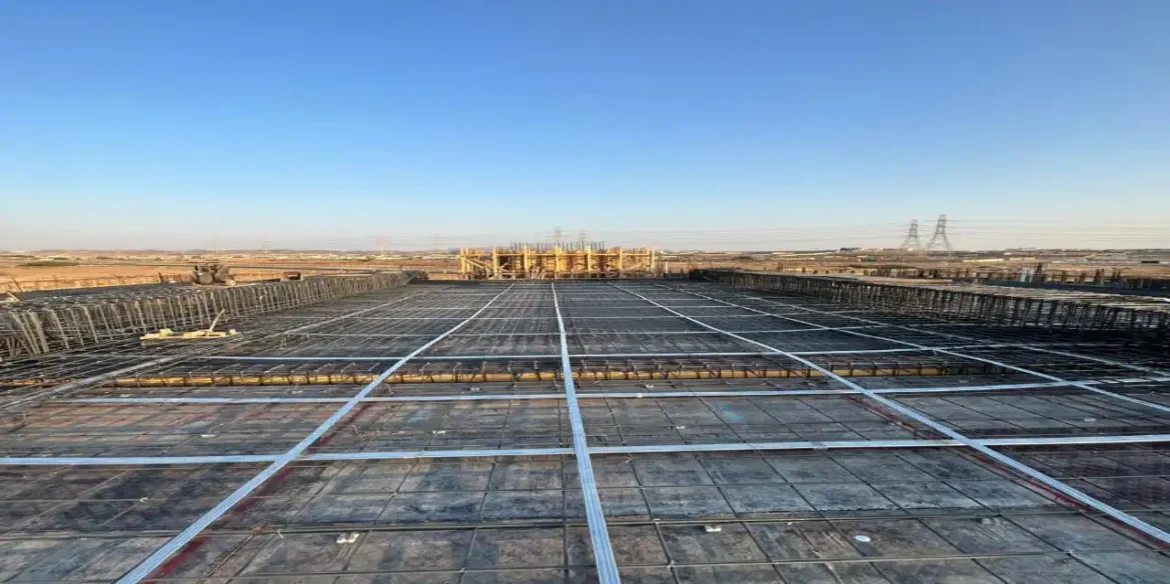
The Kingdom's massive urbanization is evident in a series of ambitious initiatives and projects, such as NEOM, The Line, the Red Sea Project, the Riyadh Metro, and Qiddiya. These projects are not conventional, but represent models of future cities and smart infrastructure.
In The Line, for example, which runs 170 kilometers in a straight line, post-tensioned concrete is an engineering necessity, enabling long-lasting slabs and continuous buildings without frequent expansion joints. This achieves visual and architectural integrity and minimizes maintenance, in line with sustainability goals.

In the Riyadh Metro project, post-tensioned concrete was used in overhead bridges and elevated pedestrian walkways. The technology helped reduce the number of piles, allowing for better traffic flow and easier implementation within a tight schedule.
In the Red Sea project, located on environmentally sensitive coastlines, post-tensioned concrete helped achieve stringent sustainability requirements, as it minimizes material use and extends the life of the structures in a marine environment with high corrosive effects.
Highlighted Applications in national projects:
- The Line Project: To realize an extended design with no breaks.
- Riyadh Metro: Minimize pillars and maximize efficiency.
- The Red Sea Project: Resisting environmental erosion and minimizing structural mass.
⸻
Compliance with the Saudi Building Code: Safety and sustainability
No engineering technology can be adopted without conforming to the requirements of the Saudi Building Code, one of the most advanced codes in the region. This code includes strict standards related to load bearing, earthquake resistance.
Practical experience has shown that post-tensioned concrete strictly complies with these requirements and in some respects is superior to conventional concrete systems, especially with regard to Bye-bye Against cracks caused by live loads or environmental influences.
In addition, the Saudi Building Code encourages the use of smart building systems that minimize operational and maintenance costs and maximize material and energy efficiency. This is where post-tensioned concrete excels, with significant savings in slab thickness and steel quantities, resulting in lighter and more efficient structures.
Aspects in which the technology is aligned with the code:
- Resistance to earthquakes and cracks.
- Efficiently withstand live and dead loads.
- Save on materials and weight.
- Matching smart building requirements.
⸻
Design and construction benefits: Beyond Steel and Concrete
One of the main reasons for the popularity of post-tensioned concrete is its ability to achieve flexible designs without compromising structural safety. By utilizing this technology, an architect or designer can free their vision from the constraints imposed by load-bearing walls or dense columns.
This type of concrete allows the creation of wide spaces of more than 10 meters between columns, providing great freedom in the arrangement of the interior space, whether in residential, commercial or service buildings.

Moreover, post-tensioned concrete reduces overall ceiling heights, which is critical in towers or projects that require a large number of floors within certain height limits. It also reduces the overall weight of the building, which reduces the stress on the soil and foundations, and directly saves costs.
Highlighted Design benefits:
- High flexibility in the internal layout of buildings.
- Reduce the number of columns and increase the openings.
- Minimize floor heights and slab thicknesses.
- Optimize load distribution and reduce stress on the soil.
⸻
Operational challenges and considerations for post-tensioned concrete
Despite the obvious advantages, the implementation of post-tensioned concrete requires precise knowledge and high-level coordination between designers, contractors, and suppliers. Tension cables must be handled with thoughtful engineering methods, channels must be free of obstructions, and the tensioning process must be carried out at the right time and pressure.
The documentation process, which is required by the Saudi Building Code, requires an accurate record of each tensioning operation, with testing to ensure quality and safety. Having an engineering staff trained and experienced in this technique is one of the success factors for any project that utilizes post-tensioned concrete.
Highlighted Challenges in implementation:
- High accuracy in cable tension and timing is required.
- Coordination between designers, contractors, and suppliers.
- The need to document tensile processes and tests.
- Strict adherence to the Saudi Building Code.
⸻
Sustainability and minimizing environmental impact
Post-tensioned concrete is in line with the modern concept of green building, reducing resource consumption and lowering the carbon footprint of projects due to the optimal use of materials. Since the slabs are thinner and less steel is needed, energy consumption during production and transportation is significantly reduced.
This has become central to Saudi Arabia's mega-projects, which are committed to building environmentally friendly facilities that match International Sustainability Standards. The use of post-tensioned concrete has become not only an engineering choice, but a strategic direction in line with the goals of Vision 2030.
Contributions Post-tensioning in sustainability:
- Reduce the amount of concrete and steel used.
- Reduce energy consumption in production and transportation.
- Increase facility life and reduce maintenance.
- Comply with green building standards.
⸻
Comparison of conventional and post-tensioned concrete systems
Economically, conventional systems differ from post-tensioning systems in the way loads and materials are distributed. In conventional systems, steel is relied upon to provide tensile strength, resulting in an increase in thickness and weight. In post-tensioned systems, steel cables provide this resistance in a more efficient manner, reducing the size of concrete sections.
On the other hand, tensile systems offer greater flexibility in controlling cracks and bends, advantages not readily available in standard systems, making them the best choice in installations that require high precision performance and stringent service conditions.
Differences intrinsic between the two systems:
- Traditional systems rely on rebar only.
- Post-tensioning provides better resistance by reducing volume.
- Fewer cracks and more control over bends.
- Higher structural efficiency and less material usage.
⸻
Engineering control and implementation quality
Careful engineering oversight is critical to the success of any project utilizing post-tensioning systems. Any defect in the tensioning process, such as exceeding the designed stresses or losing tension before stabilization, can lead to reduced structural efficiency or future issues. For this reason, these works are subject to a higher level of oversight than conventional projects.
Monitoring includes checking the condition of the cables, sewer cleanliness, recording readings, and checking the fixing of the end caps after tensioning. Concrete strength tests should be carried out at an appropriate time to ensure that it can withstand tension before the operation is carried out.
Actions Important control:
- Inspect cables and ducts before tensioning.
- Measuring pressures and documenting readings.
- Terminal head stabilization check.
- Timely concrete strength tests.
⸻
Maintenance of facilities that used post-tensioned concrete and post-implementation performance analysis
Although tensile systems are known for their long life and high efficiency, regular maintenance is necessary to ensure continued high performance. Maintenance includes checking for cracks, making sure there are no water or chemical leaks in the cable ducts, and verifying the system's stability over time.
Post-implementation performance is analyzed through techniques such as thermal imaging, ultrasound, or load tests, which give indications of the quality of the installation. Accurate documentation of each stage of implementation facilitates future audits and maintenance.
The most important Maintenance and analysis items:
- Inspect for cracks and end-heads.
- Check for sewer leaks.
- Use non-destructive techniques for verification.
- Keep detailed records of each implementation phase.
⸻
Safety and security aspects at construction sites
Performing tensile work requires a high degree of discipline and adherence to safety procedures. Dealing with enormous tensile forces requires special tools and a work environment that is free from Risks. Workers should wear personal protective equipment and make sure that the tensioning area is clear of any uninvolved personnel to avoid injuries.
A contingency plan should be in place to cover potential failures, especially those that may arise due to human error or poor materials. Having a safety engineer on site is essential to the success of critical operations.
Requirements Safety in tensile work:
- Use personal protective equipment.
- Strictly secure the tightening area.
- A contingency plan for any malfunction or cable explosion.
- Supervision of a competent safety engineer on site.
⸻
Conclusion
Post-tensioned concrete is one of the future pillars of the Saudi construction industry, offering practical, flexible and sustainable solutions. Its compliance with Saudi building code requirements and its ability to adapt to the ambitious nature of Saudi Arabia's mega-projects makes it the perfect choice for the next phase of development.
As the Kingdom continues to expand with mega infrastructure and urbanization projects, post-tensioned concrete will remain the cornerstone of future construction, driven by unparalleled design, economic and environmental efficiency
Frequently Asked Questions About Post-Tensioned Concrete
1. Is post-tensioned concrete suitable for all types of buildings?
Yes, they are used in towers, bridges, malls, and even in foundations and tunnels, especially where long openings or weight reduction is needed.
2. What is the difference between post-tensioned and pre-tensioned concrete?
In pre-tensioning, the cables are tensioned before the concrete is poured, while in post-tensioning they are tensioned after the concrete has hardened, allowing for greater flexibility in design and execution.
3. Is the cost of post-tensioned concrete higher?
The initial cost may be relatively higher, but it leads to significant savings in the long run thanks to reduced maintenance and materials.
4. How compliant are they with the Saudi Building Code?
It is fully compliant with the Saudi Building Code and has been officially adopted in many major projects in the Kingdom.
5. What skills are required to execute it?
It requires trained technical personnel, specialized tensioning equipment, as well as careful engineering supervision at all stages.
6. Does this technology accelerate project delivery?
Yes, by minimizing the number of breaks and substrates, it allows work to be done more quickly and efficiently.